Importance of Bio-regulators in Horticultural Crops
Introduction
- The growth and development of horticultural crops are controlled by hormones, also called plant growth substances or bio-regulators.
These naturally occurring or synthetic compounds influence cell division, elongation, flowering, fruiting, ripening, and dormancy. - Their judicious use in horticultural crops improves growth, yield, quality, and marketability.
Definition
- Bio-regulators (or Plant Growth Regulators – PGRs) are organic compounds, other than nutrients, which in small quantities influence the physiological processes of plants such as growth, differentiation, and development.
- They can be:
- Naturally produced (plant hormones)
- Synthetic chemicals that mimic or inhibit natural hormones.
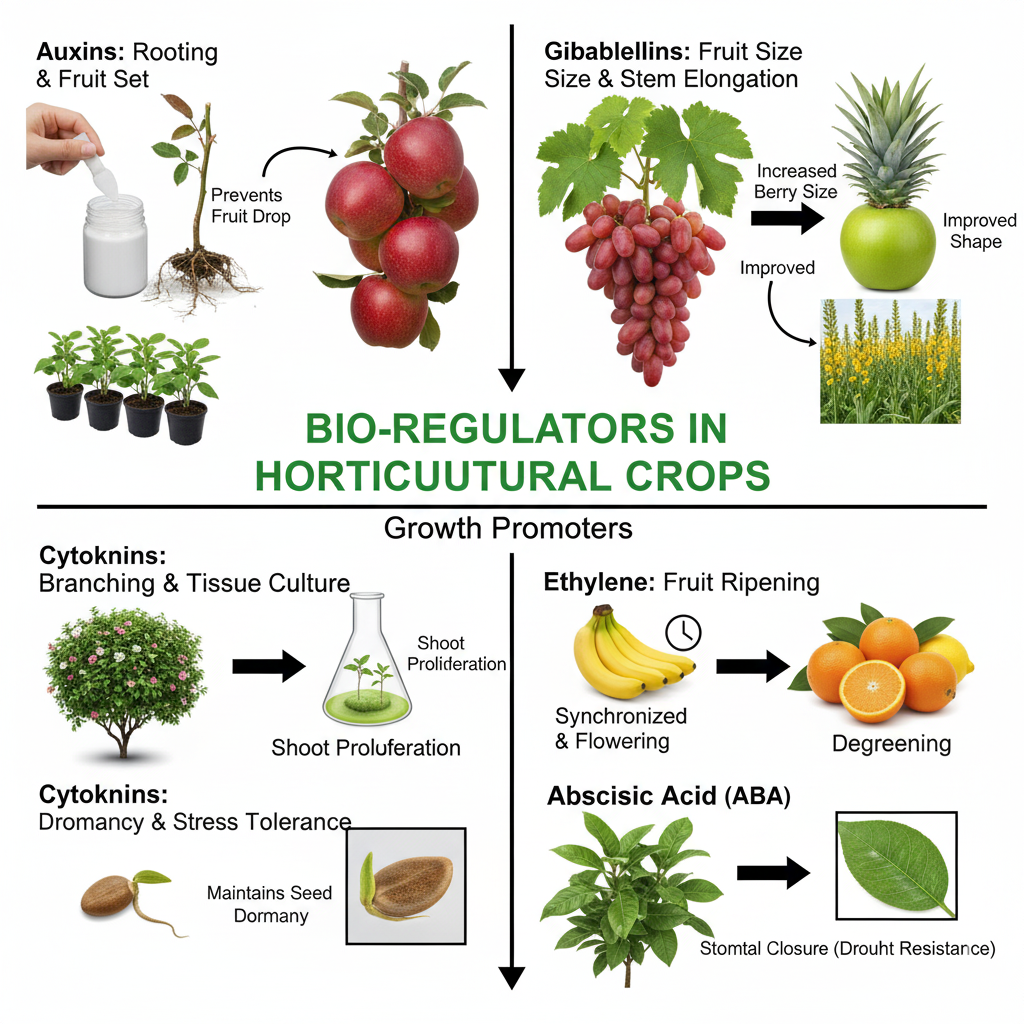
Classification of Bio-regulators
|
Group |
Examples |
General Function |
|
1. Auxins |
IAA, IBA, NAA, 2,4-D |
Cell elongation, rooting, fruit set, prevent fruit drop |
|
2. Gibberellins |
GA₃, GA₄ |
Stem elongation, breaking dormancy, fruit size improvement |
|
3. Cytokinins |
Kinetin, Benzyl Adenine (BA), Zeatin |
Cell division, delay senescence, improve fruit quality |
|
4. Ethylene |
Ethephon (Ethrel), Ethylene gas |
Fruit ripening, flower induction, abscission |
|
5. Abscisic Acid (ABA) |
Abscisic acid |
Induces dormancy, stress resistance |
|
6. Growth Retardants / Inhibitors |
CCC (Cycocel), Alar, Paclobutrazol |
Control vegetative growth, promote flowering |
|
7. Growth Promoters (Combinations) |
Mixtures of auxin + cytokinin + GA₃ |
Used in tissue culture and fruit growth regulation |
Major Functions of Bio-regulators in Horticultural Crops
Vegetative Growth Regulation
- Auxins promote cell elongation and root initiation: e.g., IBA (2000 ppm) for rooting of guava, grapes, and pomegranate cuttings.
- Gibberellins (GA₃) stimulate stem elongation and leaf expansion.
- Cytokinins promote cell division and shoot proliferation.
- Growth retardants (CCC, paclobutrazol) reduce excessive vegetative growth (e.g., in mango, citrus).
Flower Induction and Regulation
- Gibberellins (GA₃) induce flowering in non-flowering plants (e.g., pineapple).
- Paclobutrazol (PP333) promotes flowering by reducing vegetative growth in mango and citrus.
- Ethephon (Ethrel) induces flowering in pineapple (50–100 ppm).
- Cytokinins help in bud break and synchronization of flowering.
Fruit Set and Fruit Development
- Auxins (NAA, 2,4-D) induce parthenocarpic (seedless) fruit set in tomato, citrus, and grapes.
- GA₃ (25–50 ppm) increases fruit set and berry size in grapes.
- NAA (20–40 ppm) improves fruit retention and reduces premature fruit drop in mango and citrus.
Fruit Thinning and Sizing
- NAA (10–20 ppm) and 2,4-D (10 ppm) used for fruit thinning in apple and citrus to improve size and quality.
- GA₃ (50–100 ppm) increases fruit length and weight in grape, apple, and citrus.
Fruit Ripening and Degreening: Ethrel (100–500 ppm) releases ethylene, which promotes: Uniform ripening in banana, mango, and pineapple. Degreening in citrus fruits for better market appearance.
Delay in Ripening (Postharvest Management)
- Cytokinins (BA, kinetin) delay senescence and maintain green color of leaves and fruits.
- GA₃ delays ripening in banana and tomato, extending shelf life.
Breaking Dormancy
- Gibberellins (GA₃, 100 ppm) break bud dormancy in grapes, peach, and potato tubers.
- Thiourea and KNO₃ are also used as dormancy-breaking agents in temperate fruits.
Prevention of Premature Fruit Drop
- NAA (20–40 ppm) or 2,4-D (10 ppm) applied before harvesting prevent fruit drop in mango, citrus, and apple.
Rooting of Cuttings and Grafting Success
- IBA (2000 ppm) and NAA (500–1000 ppm) promote rooting in hardwood and semi-hardwood cuttings.
- Improves survival rate in propagation of guava, grapes, pomegranate, and rose.
Parthenocarpy Induction
- Auxins (NAA), Gibberellins (GA₃), and 2,4-D induce seedless fruit formation.
- Example: GA₃ induces parthenocarpy in grapes and cucumber; NAA in citrus.
Color Development and Quality Improvement
- Ethrel enhances fruit color (degreening).
- Cytokinins and GA₃ improve size, sweetness, and shelf life of fruits.
- Calcium sprays with PGRs improve firmness and reduce cracking.
Postharvest Life Extension
- Cytokinins delay leaf yellowing and fruit aging.
- GA₃ maintains firmness and delays softening.
- Ethrel regulates uniform ripening for market preparation.
Role of Bio-regulators in Different Horticultural Crops
|
Crop |
Bio-regulator & Concentration |
Purpose / Effect |
|
Mango |
Paclobutrazol (5–10 ml/tree) |
Induces flowering, controls alternate bearing |
|
Grape |
GA₃ (25–50 ppm) |
Increases berry size and fruit set |
|
Citrus |
2,4-D (10 ppm), NAA (20 ppm) |
Prevents fruit drop |
|
Banana |
Ethrel (100 ppm) |
Uniform ripening |
|
Papaya |
GA₃ (100 ppm) |
Increases fruit size |
|
Apple |
NAA (10 ppm) |
Fruit thinning |
|
Pineapple |
Ethrel (50–100 ppm) |
Flower induction |
|
Tomato |
2,4-D (10 ppm) |
Induces parthenocarpy |
|
Guava |
NAA (100 ppm) |
Reduces fruit drop |
|
Chrysanthemum / Ornamental |
CCC (500 ppm) |
Controls plant height, enhances flowering |
Methods of Application of Bio-regulators
|
Method |
Description / Example |
|
Foliar spray |
Common method for NAA, GA₃, and ethrel applications. |
|
Soil drenching |
Used for paclobutrazol (mango, citrus). |
|
Seed or cutting treatment |
Auxins like IBA for rooting. |
|
Paste application / smearing |
For localized bud treatment. |
|
Injection / trunk absorption |
For slow, controlled uptake (in perennials). |
Advantages of Using Bio-regulators
|
Benefit |
Explanation |
|
1. Early and uniform flowering |
Important for synchronization and yield stability. |
|
2. Reduced fruit drop |
Enhances yield. |
|
3. Improved fruit size and color |
Better marketability. |
|
4. Seedless fruit production |
Induces parthenocarpy. |
|
5. Stress tolerance |
Helps plants withstand drought or heat stress. |
|
6. Controlled growth |
Maintains desired plant shape and size. |
|
7. Enhanced rooting and propagation |
Improves vegetative multiplication. |
