Agro-Climatic Regional Planning
- Initiation: It was initiated in 1988 by the Planning Commission of India under the Seventh Five Year Plan.
- Objective: The regional planning was implemented on the basis of agro-climatic factors to ensure balanced regional growth across India.
- Planning Authority: The Planning Commission is headed by the Prime Minister of India.
Planning Commission
- Established: 1950 by the Government of India.
- Objective: Formulate and oversee Five-Year Plans for balanced economic development.
- Structure: Headed by the Prime Minister.
- Key Functions:
- Formulated Five-Year Plans.
- Allocated resources to various sectors and states.
- Monitored and evaluated plan implementation.
- Abolition: Dissolved in 2014, replaced by NITI Aayog.
NITI Aayog
- Established: 1st January 2015.
- Objective: Promote cooperative federalism and sustainable development.
- Structure: Headed by the Prime Minister, includes Vice Chairman, Members, and CEOs.
- Key Functions:
- Provides strategic advice for policy formulation.
- Monitors and evaluates government programs.
- Focuses on innovation, research, and sustainable growth.
- Promotes collaborative partnerships between central and state governments.
Agro-Climatic Zones (ACZ)
Definition: Agro-climatic zones are regions classified based on climatic conditions like temperature, rainfall, and humidity, which directly affect agriculture and farming practices.
Classification in India:
- According to the Planning Commission, India is divided into 15 agro-climatic zones.
- According to NARP (National Agricultural Research Project)/ ICAR (Indian Council of Agricultural Research), India is divided into 131 agro-climatic zones.
Agro-Ecological Zones (AEZ)
- Definition: Agro-ecological zones are defined based on a combination of ecological factors, including climate, soil types, topography, vegetation, and hydrological conditions. This classification looks at a wider set of ecological factors beyond just the climate.
Classification in India:
- According to NBSS&LUP (National Bureau of Soil Survey and Land Use Planning), Nagpur, Maharashtra, India. India is divided into 21 agro-ecological zones.
- According to ICAR, India is divided into 8 agro-ecological zones.
Key Differences
Focus:
- Agro-climatic zones focus mainly on climatic factors and the growing season.
- Agro-ecological zones consider a broader range of environmental factors, including soils and topography.
Purpose:
- Agro-climatic zones aim to help in crop selection and farming practices based on climate.
- Agro-ecological zones help in land use planning, conservation, and sustainable farming by understanding the entire ecological environment.
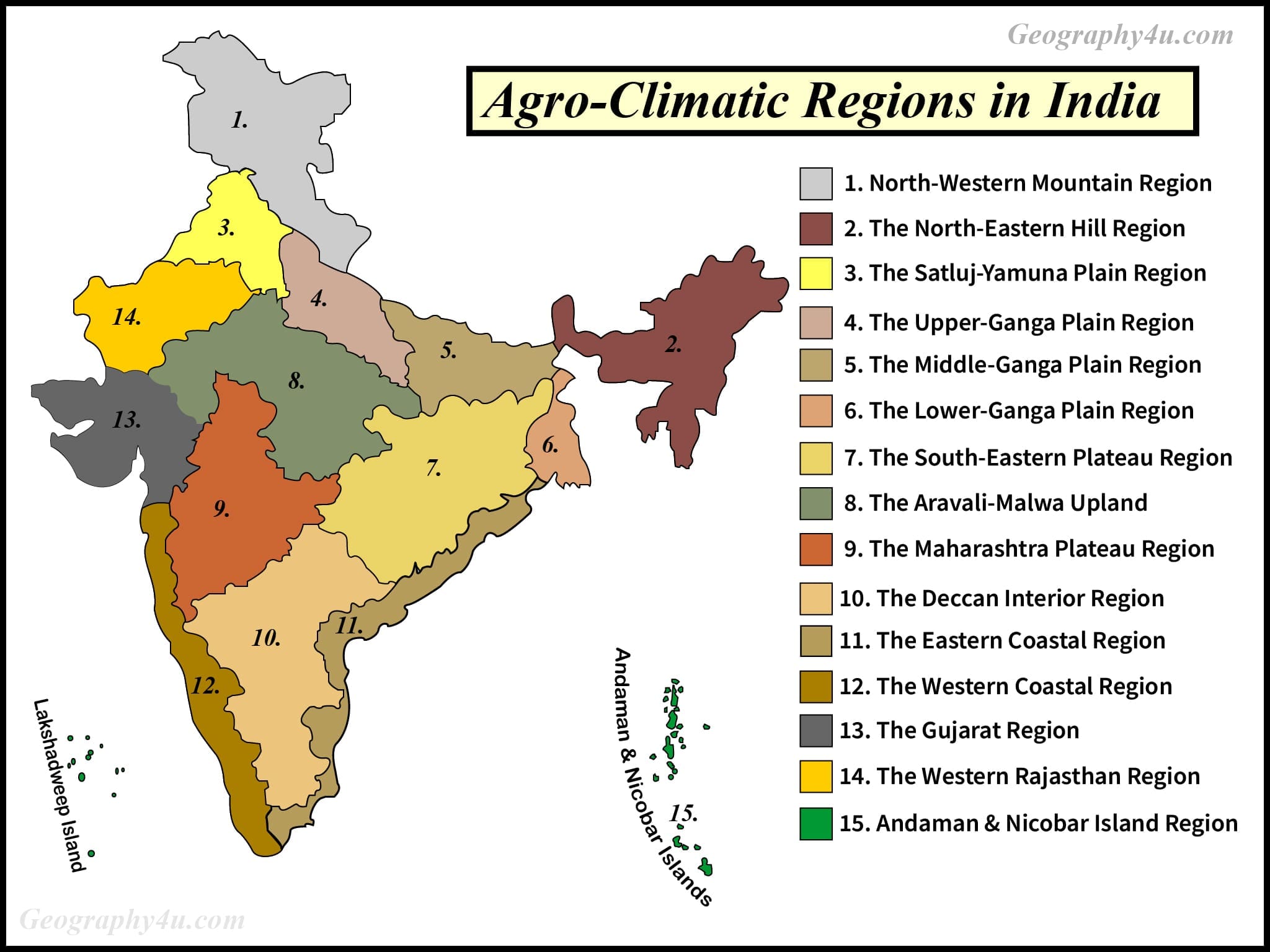
Agro-Climatic Zones of India
|
S.No |
Agro-Climatic Zone |
States Included |
Climate Description |
Annual Rainfall (mm) |
Main Crops |
|
1 |
Western Himalayan Region |
Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Uttarakhand |
Cool and humid climate with significant temperature variations due to altitude. Summers are mild, while winters can be severe with heavy snowfall. |
1,000–2,000 |
Wheat, maize, barley, fruits (apples, pears), and vegetables (potatoes, peas). |
|
2 |
Eastern Himalayan Region |
Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, Tripura, parts of West Bengal |
Humid and sub-humid climate with heavy rainfall, especially during the monsoon season. The region experiences a mild summer and cool winter. |
1,500–3,000 |
Rice, maize, millets, tea, and various horticultural crops. |
|
3 |
Lower Gangetic Plains Region |
West Bengal |
Moist humid to dry humid climate with hot summers and mild winters. The region is prone to flooding during monsoons. |
1,200–1,800 |
Rice, jute, sugarcane, pulses, and oilseeds. |
|
4 |
Middle Gangetic Plains Region |
Bihar, Eastern Uttar Pradesh |
Moist sub-humid to dry sub-humid climate with hot summers and cool winters. The region has fertile alluvial soil, making it suitable for diverse cropping. |
1,000–1,500 |
Rice, wheat, maize, pulses, and oilseeds. |
|
5 |
Upper Gangetic Plains Region |
Western and Central Uttar Pradesh |
Dry sub-humid to semi-arid climate with hot summers and cold winters. The region benefits from extensive irrigation facilities. |
800–1,200 |
Wheat, rice, sugarcane, and pulses. |
|
6 |
Trans-Gangetic Plains Region |
Punjab, Haryana, Delhi, Chandigarh, parts of Rajasthan |
Semi-arid to dry sub-humid climate with hot summers and cool winters. The region has well-developed irrigation systems, supporting intensive agriculture. |
500–1,000 |
Wheat, rice, maize, and cotton. |
|
7 |
Eastern Plateau and Hills Region |
Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Odisha, parts of Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh |
Moist sub-humid to dry sub-humid climate with moderate rainfall. The region has undulating terrain with red and lateritic soils. |
1,000–1,400 |
Rice, millets, pulses, and oilseeds. |
|
8 |
Central Plateau and Hills Region |
Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan |
Semi-arid to dry sub-humid climate with hot summers and cool winters. The region has mixed red and black soils, suitable for diverse cropping. |
600–1,000 |
Wheat, sorghum, millets, and pulses. |
|
9 |
Western Plateau and Hills Region |
Maharashtra, parts of Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan |
Semi-arid climate with hot summers and mild winters. The region has black cotton soil, ideal for certain cash crops. |
500–1,000 |
Cotton, sorghum, millets, and pulses. |
|
10 |
Southern Plateau and Hills Region |
Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu |
Semi-arid to dry sub-humid climate with moderate rainfall. The region has diverse soils, supporting various cropping systems. |
800–1,200 |
Millets, pulses, oilseeds, and cotton. |
|
11 |
East Coast Plains and Hills Region |
Coastal regions of Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu |
Semi-arid to dry sub-humid climate with hot summers and moderate to high rainfall during monsoons. The region is prone to cyclones. |
1,000–1,500 |
Rice, millets, pulses, and oilseeds. |
|
12 |
West Coast Plains and Ghats Region |
Coastal regions of Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka, Kerala |
Humid climate with heavy rainfall, especially during the monsoon season. The region has lateritic and alluvial soils. |
2,000–3,000 |
Rice, coconut, cashew, and spices. |
|
13 |
Gujarat Plains and Hills Region |
Gujarat |
Semi-arid to arid climate with hot summers and mild winters. The region has diverse soils, including black cotton soil. |
500–1,000 |
Cotton, groundnut, millets, and pulses. |
|
14 |
Western Dry Region |
Western Rajasthan |
Arid climate with extreme temperatures and very low rainfall. The region has sandy soils and is prone to droughts. |
<500 |
Millets, pulses, and drought-resistant crops. |
|
15 |
Island Region |
Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Lakshadweep |
Humid tropical climate with heavy rainfall and warm temperatures year-round. The region has sandy and loamy soils. |
2,500–3,500 |
Coconut, rice, and tropical fruits. |
Agro-Ecological Zones of India
|
AEZ No. |
Agro-Ecological Zone Name |
States/Regions Covered |
Climate Characteristics |
Soil Types |
Predominant Crops |
|
1 |
Western Himalayas |
Jammu & Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand |
Cold arid to warm sub-humid; rainfall varies from <150 mm to 2000 mm |
Shallow to deep soils |
Wheat, Maize, Paddy, Potato |
|
2 |
Western Plain, Kutch & Part of Kathiawar Peninsula |
Western Rajasthan, Southwest Haryana, parts of Gujarat |
Hot arid; rainfall 100–500 mm; high PET |
Desert soils, saline/alkaline soils |
Bajra, Gram, Wheat, Mustard |
|
3 |
Deccan Plateau, Hot Arid Region |
Parts of Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka |
Hot arid; rainfall 400–500 mm; high PET |
Red and black soils |
Jowar, Bajra, Pulses |
|
4 |
Northern Plain and Central Highlands, Hot Semi-Arid Region |
Punjab, Haryana, Delhi, Eastern Rajasthan, Western Uttar Pradesh, Northern Madhya Pradesh |
Hot semi-arid; rainfall 500–1000 mm; moderate PET |
Alluvial soils, sandy loam |
Wheat, Rice, Sugarcane, Cotton |
|
5 |
Central Highlands, Hot Semi-Arid Region |
Eastern Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat |
Hot semi-arid; rainfall 600–900 mm; moderate PET |
Medium deep black soils |
Soybean, Wheat, Sorghum |
|
6 |
Deccan Plateau, Hot Semi-Arid Region |
Maharashtra, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana |
Hot semi-arid; rainfall 600–1000 mm; moderate PET |
Shallow to medium black soils |
Cotton, Jowar, Bajra, Pulses |
|
7 |
Deccan Plateau, Hot Moist Semi-Arid Region |
Parts of Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Tamil Nadu |
Hot moist semi-arid; rainfall 700–1100 mm; moderate PET |
Red and black soils |
Rice, Groundnut, Millets |
|
8 |
Eastern Ghats, Tamil Nadu Uplands, Hot Moist Semi-Arid Region |
Tamil Nadu, parts of Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh |
Hot moist semi-arid; rainfall 800–1200 mm; moderate PET |
Red loamy soils |
Rice, Ragi, Groundnut |
|
9 |
Northern Plain, Hot Sub-Humid Region |
Uttar Pradesh, Bihar |
Hot sub-humid; rainfall 1000–1200 mm; moderate PET |
Alluvial soils |
Rice, Wheat, Sugarcane |
|
10 |
Central Highlands, Malwa and Bundelkhand, Hot Sub-Humid Region |
Madhya Pradesh, parts of Uttar Pradesh |
Hot sub-humid; rainfall 1000–1200 mm; moderate PET |
Medium and deep black soils |
Soybean, Wheat, Chickpea |
|
11 |
Eastern Plateau, Chhattisgarh, Hot Sub-Humid Region |
Chhattisgarh, parts of Odisha, Maharashtra |
Hot sub-humid; rainfall 1200–1600 mm; moderate PET |
Red and yellow soils |
Rice, Maize, Pulses |
|
12 |
Eastern Plateau, Chotanagpur, Hot Sub-Humid Region |
Jharkhand, parts of West Bengal, Odisha |
Hot sub-humid; rainfall 1100–1500 mm; moderate PET |
Red loamy soils |
Rice, Maize, Pulses |
|
13 |
Eastern Plain, Hot Sub-Humid Region |
Eastern Uttar Pradesh, Bihar |
Hot sub-humid; rainfall 1200–1400 mm; moderate PET |
Alluvial soils |
Rice, Wheat, Sugarcane |
|
14 |
Western Himalayas, Warm Sub-Humid Region |
Jammu & Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand |
Warm sub-humid; rainfall 1600–2000 mm; exceeds PET |
Brown forest and podzolic soils |
Wheat, Maize, Barley |
|
15 |
Assam and Bengal Plains, Hot Humid Region |
Assam, West Bengal |
Hot humid; rainfall 1400–2000 mm; high humidity |
Alluvial soils |
Rice, Jute, Tea |
|
16 |
Eastern Himalayas, Warm Humid Region |
Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim, parts of Assam and West Bengal |
Warm humid; rainfall >2000 mm; occurs throughout the year |
Brown hill soils |
Rice, Maize, Millet |
|
17 |
North-Eastern Hills, Purvanchal, Warm Humid Region |
Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram, Tripura, Meghalaya |
Warm humid; rainfall 1600–2600 mm; exceeds PET |
Red and lateritic soils |
Rice, Maize, Pulses |
|
18 |
Eastern Coastal Plain, Hot Sub-Humid Region |
Coastal regions of Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Odisha |
Hot sub-humid; rainfall 1000–1600 mm; moderate PET |
Alluvial and coastal sandy soils |
Rice, Groundnut, Coconut |
|
19 |
Western Ghats and Coastal Plain, Hot Humid Region |
Western coastal regions of Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka, Kerala |
Hot humid; rainfall >2000 mm; high humidity |
Red laterite and alluvial soils |
Rice, Coconut, Spices |
|
20 |
Islands of Andaman, Nicobar, and Lakshadweep, Hot Humid Region |
Andaman & Nicobar Islands, Lakshadweep |
Hot humid; rainfall 1600–3000 mm; occurs throughout the year |
Red loam to sandy loam soils |
Coconut, Arecanut, Tropical Fruits |

