Bulk Density and Particle Density
- Introduction
The density of soil is a key physical property that reflects how compact or loose the soil is.
It affects porosity, aeration, water movement, root penetration, and tillage operations.
Two important types of soil density are:
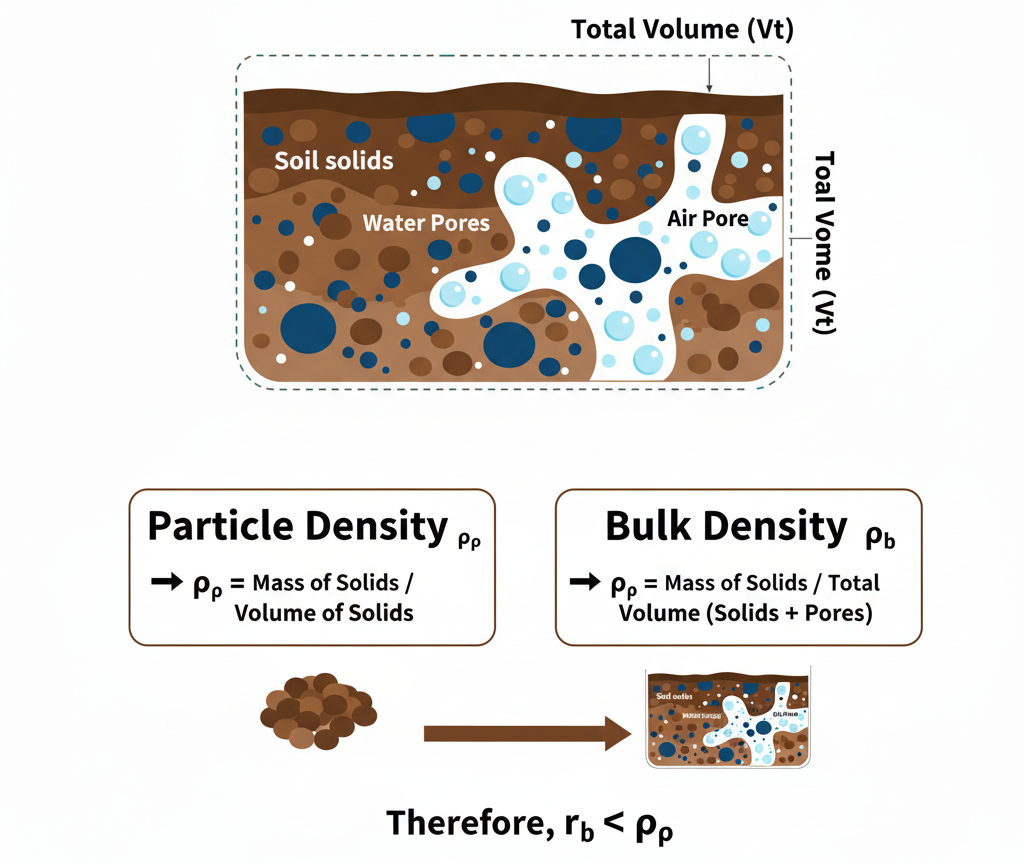
- Particle Density (ρp) – mass per unit volume of soil solids only.
- Bulk Density (ρb) – mass per unit volume of soil (including pores).
- Particle Density (ρp)
- Definition: Particle Density is the mass of solid soil particles per unit volume of those particles, excluding pore spaces.
- Ρp = Mass of soil solids (Ms) / Volume of soil solids (Vs)
- Units: g/cm³ or Mg/m³
Typical Values:
|
Soil Type |
Particle Density (g/cm³) |
|
Mineral soils (normal) |
2.60 – 2.70 |
|
Quartz-dominated soils |
2.65 |
|
Organic soils |
1.2 – 1.5 |
|
Clay soils rich in Fe/Al oxides |
2.8 – 3.0 |
Note: Quartz (SiO₂), the dominant mineral in most soils, has a density of about 2.65 g/cm³, which is considered the standard value for mineral soils.
- Bulk Density (ρb)
- Definition: Bulk Density is the mass of oven-dry soil per unit total volume of soil, including both solid particles and pore spaces.
- Ρb = Mass of oven-dry soil (Ms) / Total volume (solids + pores) (Vt)
- Units: g/cm³ or Mg/m³
Typical Values:
|
Soil Type |
Bulk Density (g/cm³) |
|
Sandy soils |
1.60 – 1.80 |
|
Loamy soils |
1.30 – 1.50 |
|
Clayey soils |
1.10 – 1.30 |
|
Organic soils |
0.50 – 1.00 |
- Relationship Between Bulk Density, Particle Density, and Porosity
- The porosity (n) of soil is the percentage of pore space in the total volume of soil.
- N = (1−ρb / ρp) ×100
- Example: If; ρb = 1.40 g/cm³. ρp = 2.65 g/cm³
- Then, n = (1−1.40/2.65)×100 =47.2%
5. Methods of Determination
Particle Density
- Pycnometer Method
- Soil sample is weighed and placed in a pycnometer filled with water.
- Volume displacement gives the volume of solids.
- Particle density = Mass / Volume of solids.
Bulk Density
- Core Method (Commonly used)
- A known-volume cylindrical core is driven into the soil.
- The core is taken out, oven-dried (105°C for 24 hours), and weighed.
- Ρb = Ms / Vt
- where Ms = oven-dry mass of soil, Vt = total volume of the core.
- Clod Method: A natural soil clod is coated with paraffin wax and its volume determined by water displacement.
- Excavation Method: For loose sandy soils; volume of hole measured by filling it with sand or water.
- Factors Affecting Bulk Density
|
Factor |
Effect |
|
Soil texture |
Sandy soils → high ρb; Clayey soils → low ρb |
|
Organic matter |
Increases porosity → decreases ρb |
|
Soil structure |
Granular → low ρb; compact → high ρb |
|
Depth |
ρb increases with depth due to compaction |
|
Tillage |
Reduces ρb temporarily by loosening soil |
|
Soil compaction |
Increases ρb, reduces porosity and aeration |
- Relationship Between Density and Porosity
|
Soil Type |
ρp (g/cm³) |
ρb (g/cm³) |
Porosity (%) |
|
Sand |
2.65 |
1.75 |
34 |
|
Loam |
2.65 |
1.40 |
47 |
|
Clay |
2.70 |
1.20 |
56 |
|
Organic soil |
1.40 |
0.80 |
43 |
- Agricultural Importance
|
Aspect |
Effect / Importance |
|
Porosity and aeration |
Lower ρb → more pore space → better aeration |
|
Root growth |
Optimum ρb (1.2–1.4) ensures easy root penetration |
|
Water movement |
Low ρb promotes infiltration and percolation |
|
Soil compaction |
High ρb (>1.6) restricts air and root movement |
|
Fertility |
Influences microbial activity and nutrient availability |
|
Engineering uses |
Helps calculate soil weight and load-bearing capacity |
- Comparison Between Bulk Density and Particle Density
|
Property |
Bulk Density (ρb) |
Particle Density (ρp) |
|
Definition |
Mass of dry soil per unit total volume (solids + pores) |
Mass of soil solids per unit volume of solids only |
|
Includes pores? |
Yes |
No |
|
Typical value (mineral soil) |
1.1 – 1.6 g/cm³ |
2.6 – 2.7 g/cm³ |
|
Affected by texture and structure? |
Yes |
No |
|
Influences |
Porosity, compaction, aeration |
Mostly constant, used for calculations |
|
Standard for mineral soil |
Variable |
2.65 g/cm³ (quartz reference) |
- Ideal Bulk Density for Plant Growth
|
Soil Texture |
Ideal Bulk Density (g/cm³) |
Root Growth Condition |
|
Sandy |
1.4 – 1.6 |
Moderate |
|
Loamy |
1.2 – 1.4 |
Ideal |
|
Clayey |
1.1 – 1.3 |
Good |
|
Organic |
< 1.0 |
Excellent |
Key Points to Remember
- Particle Density (ρp) ≈ 65 g/cm³ for mineral soils.
- Bulk Density (ρb) = 1–1.6 g/cm³ (varies with texture).
- Porosity (%) = (1−ρb/ρp)×100(1 – ρb/ρp) × 100(1−ρb/ρp)×100.
- Low ρb → good structure and aeration.
- High ρb (>1.6) → compaction, poor root growth.
