Solar Photovoltaic (PV) System
Definition; Solar Photovoltaic (PV) System is a renewable energy technology that converts solar energy directly into electrical energy using semiconductor materials like silicon through the photovoltaic effect.
Principle – Photovoltaic Effect; The photovoltaic effect is the phenomenon in which electrons are ejected from a material (typically silicon) when it is exposed to sunlight, creating an electric current.
🌞 Sunlight → Electron Excitation → DC Electricity
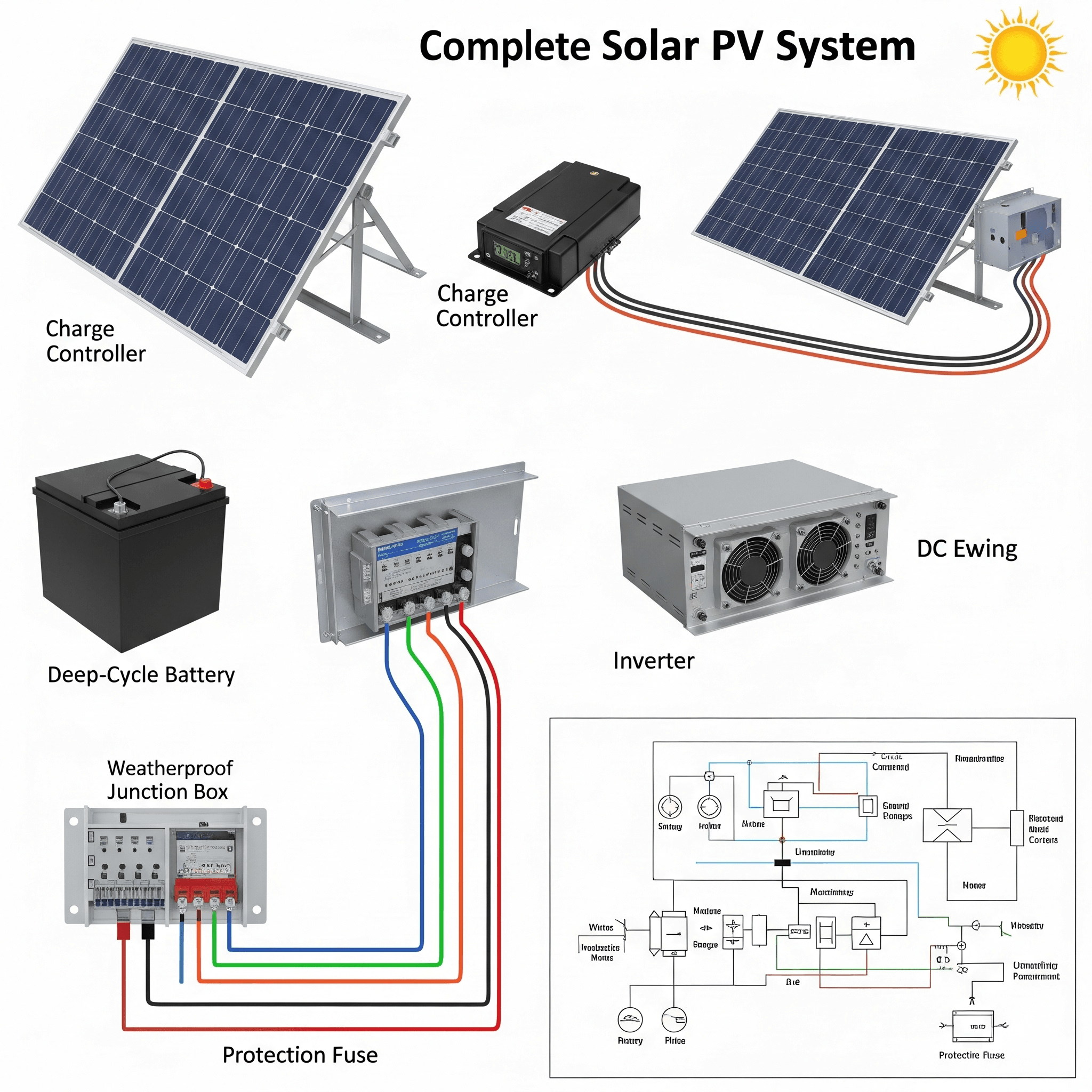
Components of Solar PV System
|
Component |
Function |
|
Solar Panel / PV Module |
Converts sunlight into DC electricity |
|
Charge Controller |
Regulates voltage and current from panels to batteries |
|
Battery (optional) |
Stores DC electricity for later use |
|
Inverter |
Converts DC electricity to AC for home/industrial use |
|
Mounting Structure |
Holds PV modules at optimal angle |
|
Cables & Junction Box |
Connects and protects the system components |
Types of Solar PV Systems
|
Type |
Description |
Key Feature |
|
Off-Grid System |
Not connected to utility grid |
Requires battery storage |
|
Grid-Tied System |
Connected to main electricity grid |
No batteries needed |
|
Hybrid System |
Combines solar, battery & grid |
Ensures power even during outages |
|
Building Integrated PV (BIPV) |
Integrated into building façade or rooftop |
Aesthetic and space-saving |
Working of a Solar PV System
- Sunlight falls on the solar panels.
- Panels generate DC electricity via the photovoltaic effect.
- If connected to an inverter, the DC is converted to AC.
- AC power is used to run appliances, and excess can be stored (off-grid) or exported to the grid (grid-tied).
Types of PV Technologies
|
Type |
Material |
Efficiency |
Remarks |
|
Monocrystalline Silicon |
Single crystal silicon |
18–22% |
High efficiency, costly |
|
Polycrystalline Silicon |
Multiple crystals |
15–17% |
Moderate cost |
|
Thin Film (CdTe, a-Si) |
Amorphous or layered |
10–12% |
Flexible, lightweight |
|
Perovskite Solar Cells |
Hybrid organic-inorganic |
20%+ (lab) |
Emerging tech |
Applications of Solar PV Systems
Domestic Applications
- Lighting, fans, TVs, refrigerators
- Solar rooftop systems (subsidized in India)
- Solar water pumping for irrigation
Commercial/Industrial
- Office lighting and backup
- Telecom towers and data centers
- Cold storage, grain dryers
Agricultural Applications
|
Application |
Description |
|
Solar Water Pumps |
For irrigation and drinking water in remote areas |
|
Solar Electric Fencing |
To protect crops from wild animals |
|
Solar Dryers |
Drying agricultural produce efficiently |
|
Solar Milk Chillers |
For preserving milk in rural dairy farms |
|
Solar Cold Storage |
To store fruits and vegetables with minimal loss |
Public Utilities
- Street lights
- Traffic signals
- Remote weather stations
- Railway signaling
Remote Areas and Defense
- Border areas, forest posts
- Disaster relief and refugee camps
Advantages of Solar PV Systems
- Abundant and Free solar energy
- Environmentally friendly, zero emissions
- Modular and scalable: Add more panels as needed
- Low maintenance
- Suitable for off-grid and grid-connected systems
- Ideal for remote agricultural use
Limitations
- High initial installation cost
- Output depends on weather/sunlight
- Efficiency limited to 15–22% in common panels
- Battery storage can be expensive and has limited life
- Requires space and orientation for best performance
Performance Parameters
|
Parameter |
Typical Value |
|
Panel Efficiency |
15–22% |
|
Temperature Coefficient |
-0.3 to -0.5%/°C |
|
Life of PV Module |
25+ years |
|
Inverter Life |
10–15 years |
|
Battery Life |
3–7 years (if used) |
Government Initiatives in India
- PM-KUSUM Scheme – Solar pumps for farmers
- Rooftop Solar Programme (MNRE)
- Subsidy schemes for residential and institutional users
- National Solar Mission – Target of 100 GW solar capacity
Recent Advancements
- Bifacial solar panels – Capture sunlight from both sides
- Floating solar PV – Installed on water bodies
- Tracking systems – Panels move with sun for max output
- Perovskite and Organic PV cells – High efficiency, flexible
Solar PV vs Solar Thermal
|
Feature |
Solar PV |
Solar Thermal |
|
Output |
Electricity |
Heat |
|
Use |
Lights, appliances |
Water heating, space heating |
|
Efficiency |
15–22% |
30–70% |
|
Cost |
High upfront |
Low to moderate |
|
Technology |
Semiconductor |
Heat collectors |
