A) Air Cleaning System in I.C. Engines 🚜
Need for an Air Cleaning System
- In an Internal Combustion (I.C.) engine, clean air is essential for efficient combustion.
- Dust, dirt, and debris in the intake air can cause wear and damage to engine components like cylinders, pistons, and valves.
- An air cleaner (air filter) removes impurities from the incoming air before mixing it with fuel in the carburetor or intake manifold.
Types of Air Cleaning Systems
There are mainly three types of air filters used in tractors and I.C. engines:
- Oil Bath Air Cleaner
- Used in older tractors and heavy-duty engines.
- Incoming air passes through an oil bath, where dust particles get trapped in the oil.
- The clean air moves upward and enters the carburetor or intake manifold.
Advantages:
- Highly effective for removing fine dust particles.
- Works well in dusty environments.
- Long-lasting and reusable (clean and refill with oil).
Disadvantages:
- Requires frequent cleaning.
- Oil can get contaminated over time.
- Dry Type Air Cleaner
- Uses a paper or foam filter element to trap dust and dirt.
- Commonly used in modern tractors and vehicles.
- Air passes through the filter, and dust gets trapped in the filter material.
Advantages:
Low maintenance, only requires replacement.
More compact and efficient.
No need for oil.
Disadvantages:
Needs frequent replacement.
Less effective in very dusty conditions.
- Cyclone Type (Pre-Cleaner) Air Cleaner
- Works on centrifugal force to remove large dust particles before air reaches the main filter.
- Often used along with dry or oil bath air filters for better performance.
- Heavy dust particles are thrown to the outer walls and collected in a dust bowl.
Advantages:
Increases the lifespan of the main filter.
Effective in high-dust environments like agriculture and construction.
Reduces maintenance costs.
Disadvantages:
Needs regular emptying of the dust bowl.
Cannot filter very fine particles alone.
Comparison of Different Air Cleaning Systems
|
Feature |
Oil Bath Air Cleaner |
Dry Type Air Cleaner |
Cyclone Air Cleaner |
|
Maintenance |
Requires oil change |
Needs filter replacement |
Needs dust bowl cleaning |
|
Effectiveness |
High (best for dusty areas) |
Moderate (best for clean environments) |
Moderate (works as pre-cleaner) |
|
Cost |
Low |
High |
Moderate |
|
Usage |
Older tractors, heavy-duty vehicles |
Modern tractors, cars |
Combined with other filters |
Maintenance Tips for Air Cleaning System
Check and clean the air filter regularly.
Replace dry filters when clogged.
Refill and clean oil bath filters as needed.
Inspect air intake pipes for leaks or damage.
Use pre-cleaners in dusty environments to extend filter life.
B. Cooling System of I.C. Engines in Tractors
Need for Cooling System
- The combustion process in an internal combustion (I.C.) engine generates high temperatures (up to 2500°C).
- If not cooled, excessive heat can damage engine components like pistons, cylinders, and valves.
- The cooling system helps maintain optimal engine temperature for efficient performance and longevity.
Types of Cooling Systems in Tractors
There are mainly two types of cooling systems used in tractors:
- Air Cooling System
- Heat is dissipated using fins attached to the engine cylinder.
- Cooling fan directs airflow over the fins to remove heat.
- Commonly used in small tractors and motorcycles.
Advantages:
Simple design, no radiator required.
Lighter in weight, low maintenance.
Effective in cold weather.
Disadvantages:
Less efficient in high temperatures.
Requires a strong airflow, limiting engine size.
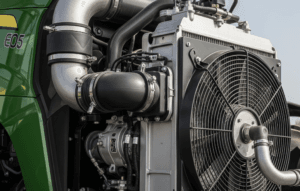
- Liquid Cooling System (Water Cooling)
- Uses water or coolant to absorb engine heat.
- The heated coolant passes through a radiator, where airflow cools it.
- A water pump circulates coolant, and a thermostat regulates temperature.
Advantages:
More effective cooling for heavy-duty engines.
Suitable for all weather conditions.
Maintains uniform engine temperature.
Disadvantages:
More complex, requires maintenance.
Water leakage can cause engine failure.
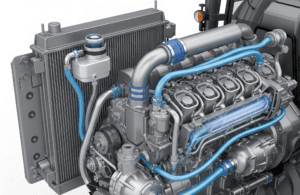
Components of a Liquid Cooling System
- Radiator – Cools down the hot coolant by airflow.
- Water Pump – Circulates coolant through the engine and radiator.
- Thermostat Valve – Maintains engine temperature by controlling coolant flow.
- Fan – Increases air circulation over the radiator.
- Coolant (Water + Antifreeze) – Absorbs engine heat and prevents freezing in winter.
- Hoses and Pipes – Transport coolant between the engine and radiator.
Comparison of Air and Liquid Cooling Systems
|
Feature |
Air Cooling System |
Liquid Cooling System |
|
Cooling Medium |
Air |
Water/Coolant |
|
Efficiency |
Less efficient in high temperatures |
More efficient |
|
Maintenance |
Low |
Requires regular coolant checks |
|
Application |
Small tractors, bikes |
Heavy tractors, cars |
Maintenance Tips for Tractor Cooling System
- Check radiator coolant level regularly.
- Clean radiator fins to avoid clogging.
- Inspect hoses for leaks and cracks.
- Ensure the thermostat is functioning properly.
- Flush and replace coolant periodically.
