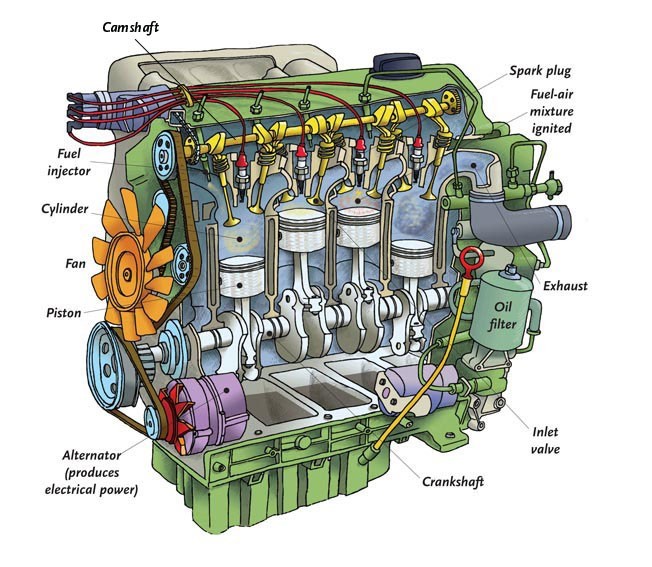
The internal combustion (I.C.) engine consists of several essential components that work together to convert fuel into mechanical energy. Here’s a study of the primary components of an I.C. engine:
- Cylinder
- Function: The cylinder is the central part of the engine where combustion occurs. It houses the piston and is where the fuel-air mixture is burned to create power.
- Types: Engine cylinders can be arranged in different configurations (inline, V-type, opposed, etc.).
- Materials: Typically made of cast iron or aluminum alloys for durability and heat resistance.
- Piston
- Function: The piston moves up and down within the cylinder, converting the pressure from the combustion process into mechanical motion. This motion drives the crankshaft.
- Design: It has rings to seal the combustion chamber and reduce friction between the piston and cylinder wall.
- Materials: Usually made from aluminum alloys to balance strength, weight, and heat conduction.
- Crankshaft
- Function: The crankshaft converts the reciprocating motion of the piston into rotational motion that drives the vehicle’s wheels or other machinery.
- Design: It consists of multiple cranks (arms) connected to the main shaft, with counterweights to balance the engine’s motion.
- Materials: Typically made from forged steel for strength and durability.
- Connecting Rod
- Function: The connecting rod connects the piston to the crankshaft. It transfers the force generated by the piston to the crankshaft.
- Design: It’s typically a long, narrow piece of metal with a bearing at each end.
- Materials: Usually made from high-strength steel or alloys to withstand stress.
- Valves (Inlet & Exhaust)
- Function: Valves control the entry of the air-fuel mixture into the cylinder (intake valve) and the exit of exhaust gases (exhaust valve). They open and close at precise timings during the engine cycle.
- Types:
- Inlet Valve: Allows the air-fuel mixture into the cylinder.
- Exhaust Valve: Allows combustion gases to exit the cylinder.
- Materials: Typically made of heat-resistant steel alloys.
- Camshaft
- Function: The camshaft operates the valves by pushing the cam followers or tappets, which in turn push the valves open and closed at the correct time in the engine cycle.
- Design: It has a series of cams (lobes) that rotate in sync with the crankshaft.
- Materials: Usually made of cast iron, steel, or hardened alloys for durability.
- Cylinder Head
- Function: The cylinder head seals the top of the cylinder and contains the intake and exhaust valves, spark plugs, and fuel injectors.
- Design: It has various passages for the intake and exhaust gases and may contain coolant channels for cooling.
- Materials: Typically made of cast iron or aluminum alloys.
- Spark Plug
- Function: In spark-ignition engines, the spark plug ignites the compressed air-fuel mixture in the cylinder by producing a spark.
- Design: It consists of a metal threaded shell, an insulator, and a center electrode.
- Materials: Made from durable materials like ceramic and copper or platinum for the electrode.
- Fuel Injector (or Carburetor)
- Function: The fuel injector (in modern engines) or carburetor (in older engines) delivers the air-fuel mixture into the combustion chamber.
- Fuel Injector: It sprays the fuel directly into the cylinder or intake manifold in a precise quantity and atomization.
- Carburetor: Mixes air and fuel in the right proportion before entering the cylinder.
- Materials: The fuel injector is typically made from stainless steel or plastic, while carburetors are made from aluminum alloys.
- Timing Belt/Chain
- Function: The timing belt or chain synchronizes the rotation of the crankshaft and camshaft(s) to ensure that the valves open and close at the correct times relative to the position of the piston.
- Materials: Timing belts are typically made of rubber with reinforced fibers, while timing chains are made from steel.
- Lubrication System (Oil Pump & Oil)
- Function: The lubrication system ensures that all moving parts in the engine (such as the piston, crankshaft, and valves) are properly lubricated to reduce friction and wear.
- Components: Includes the oil pump, oil filter, and oil passages.
- Materials: Engine oil is typically made from mineral or synthetic base oils with additives for performance and protection.
- Cooling System (Radiator, Thermostat, Water Pump)
- Function: The cooling system regulates the temperature of the engine by removing excess heat generated during combustion.
- Components: Includes the radiator, thermostat, water pump, and coolant.
- Materials: Radiators are often made of aluminum, while hoses are made from rubber or silicone.
- Exhaust System
- Function: The exhaust system channels the hot gases produced during combustion from the engine out to the atmosphere, often passing through a muffler to reduce noise and a catalytic converter to reduce harmful emissions.
- Components: Includes the exhaust manifold, muffler, and catalytic converter.
- Materials: Exhaust components are typically made of stainless steel or aluminum for heat resistance and durability.
- Flywheel
- Function: The flywheel stores rotational energy and smooths out the engine’s power delivery. It helps maintain momentum during the engine’s cycles and reduces vibrations.
- Design: It’s a heavy, rotating disk mounted on the end of the crankshaft.
- Materials: Usually made of steel or cast iron.
- Oil Filter
- Function: The oil filter cleans the engine oil by trapping contaminants such as dirt, metal particles, and carbon build-up.
- Design: A cylindrical filter that traps impurities while allowing clean oil to pass through.
- Materials: It typically consists of paper, fiber, and metal components.
- Air Filter
- Function: The air filter prevents dust, dirt, and debris from entering the engine’s air intake, ensuring clean air for combustion.
- Design: It’s made of a pleated paper or foam material to maximize filtration surface area.
- Materials: Usually made from paper, cotton, or foam.
